1.3 Crankshaft
DETROIT DIESEL 53
cracks must be rejected.
Several methods of
determining the presence of minute cracks not visible to
the eye are outlined below.
Magnetic Particle Method : The part is magnetized
and then covered with a fine magnetic powder or
solution. Flaws, such as cracks, form a small local
magnet which causes the magnetic particles in the
powder or solution to gather there, effectively marking
the crack. The crankshaft must be demagnetized after
the test.
Fluorescent Magnetic Particle Method :
This method is similar to the magnetic particle method,
but is more sensitive since it employs magnetic particles
which are fluorescent and glow under "black. light".
Very fine cracks that may be missed under the first
method, especially on discolored or dark surfaces, will
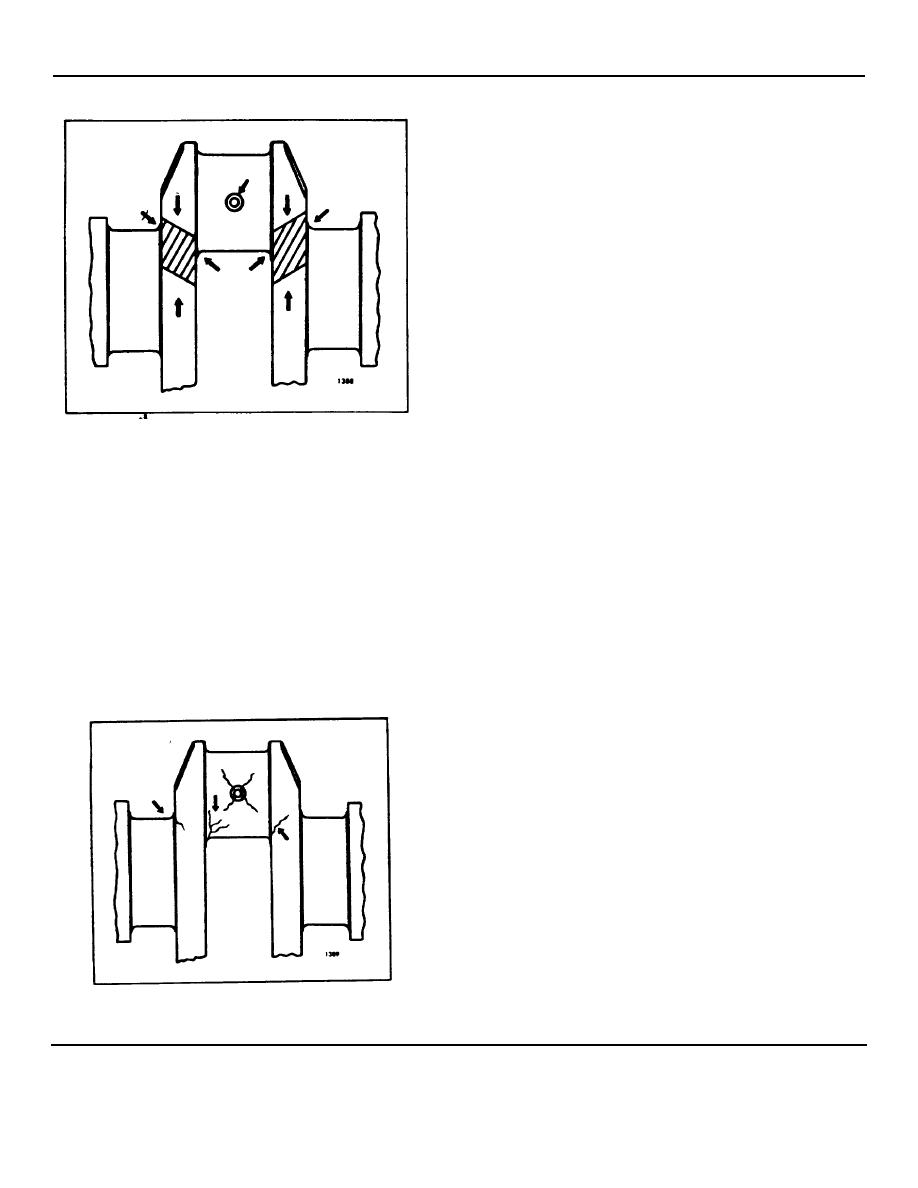
Fig. 4.- Critical Crankshaft Loading Zones
be disclosed under the "black light".
(with new shells) exceeds .0040" the crankshaft must be
Fluorescent Penetrant Method: This is a method
reground. Also, if the journal taper or out-of-round is
which may be used on non-magnetic materials such as
greater than .003", the crankshaft must be reground.
stainless steel, aluminum and plastics.
A highly
Measurements of the crankshaft should be accurate to
fluorescent liquid penetrant is applied to the part. Then,
the nearest .002".
the excess penetrant is wiped off and the part is dried.
A developing powder is then applied which helps to draw
the penetrant out of the flaws by capillary action.
Inspection is carried out under black light".
Inspection for Cracks
A majority of indications revealed by the above
Carefully check the crankshaft for cracks which start at
inspection methods are normal and harmless and only
an oil hole and follow the journal surface at an angle of
45to the axis. Any crankshaft with such
Fig. 6. - Crankshaft Fatigue Cracks
1972 General Motors Corp.
Page 4


